猪繁殖与呼吸综合征的监测与诊断(3)
(接上期2)
4. Pathological evaluation病理学评估
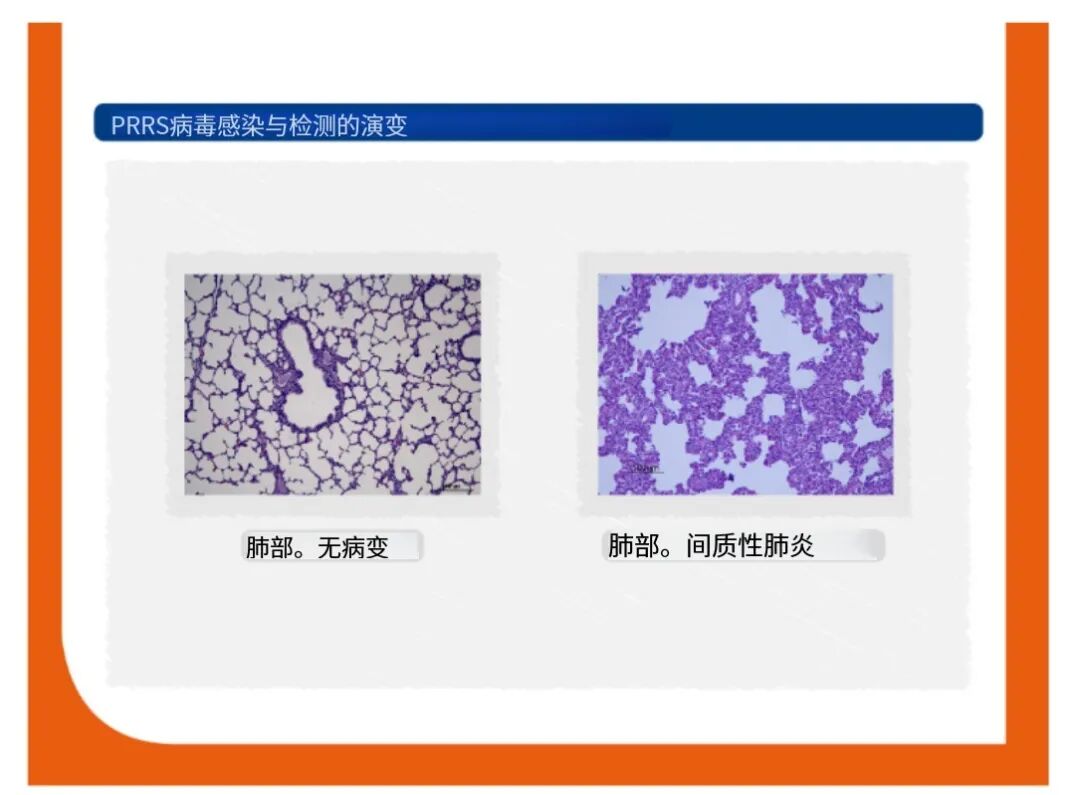
Gross lesions of interstitial pneumonia and enlarged lymph nodes due to PRRS infection may be observed. However, these lesions can be also observed during other infections.在蓝耳病的病理变化中,我们可以看到严重的间质性肺炎和淋巴结肿大,但是这些病变在其他疾病中也可以看到。
As previously mentioned, there are no pathognomonic gross lesions in lungs from pigs suffering PRRS respiratory outbreaks, neither in sows or aborted fetuses from PRRS reproductive failures.如前所述,无论是蓝耳感染后引起仔猪的呼吸症状,还是感染导致的母猪流产或流产胎儿都没有可以作为确诊的特征性病变。
Microscopically, interstitial pneumonia is the primary lesion, but it is nonspecific for PRRS virus. 显微镜下,间质性肺炎为原发病变,但并不是PRRS特征性病变。
5. Detection of virus病毒检测
Identification of PRRS virus can be accomplished by the detection of viral proteins (antigen), by virus isolation and by the detection of nucleic acids.PRRSV的鉴定,可以通过病毒的蛋白,核酸以及病毒分离进行。
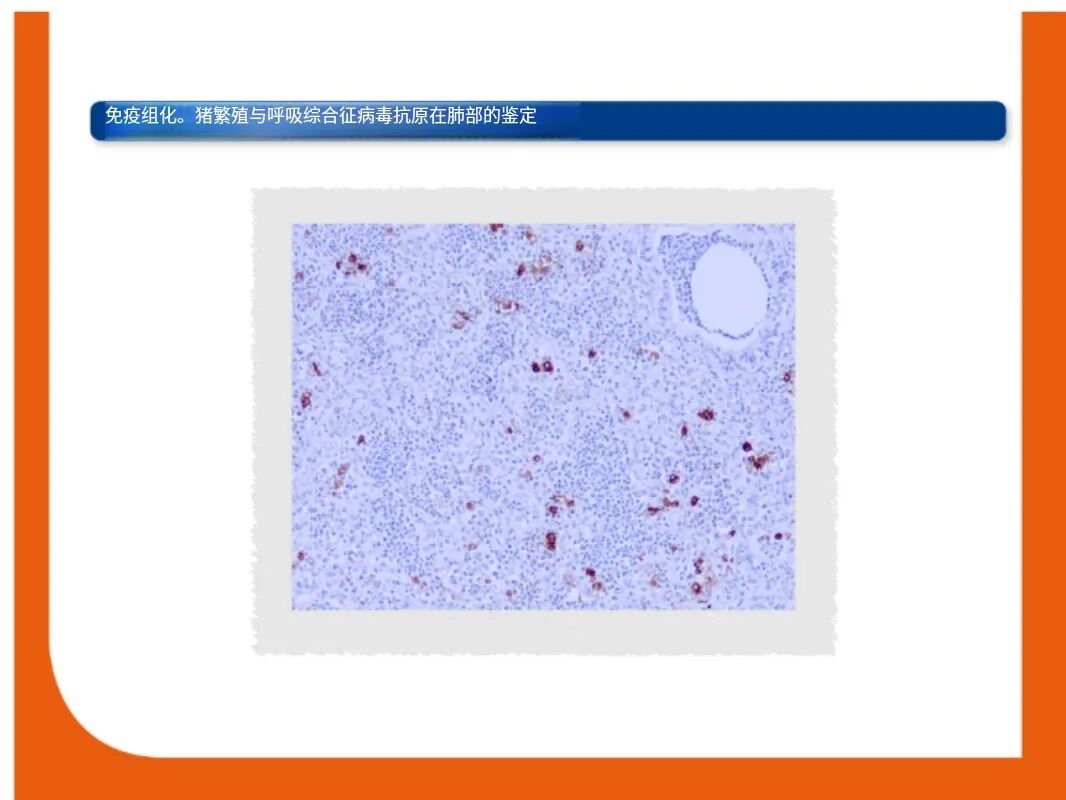
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) and in-situ hybridization (ISH)免疫组化和原位杂交
PRRS virus antigen or nucleic acid can be detected in tissues by IHC and ISH, respectively. The relationship between viral detection and lesions can be established by a combination of IHC or ISH and histopathology. PRRSV抗原或核酸可分别通过免疫组化和原位杂交进行检测。病毒检测与病理变化之间的关系可以通过IHC或ISH与组织病理学的结合分析来建立。
Virus isolation and titration病毒分离和滴度测定
Whereas PRRSV2 strains can be isolated in both porcine alveolar macrophages and sublines of the African monkey kidney cell line (CL-2621 and MARC-145), some PRRSV1 and European-like viruses can only be isolated in porcine alveolar macrophages.PRRSV-2可以通过CL-262和MARC-145细胞进行病毒的分离,不过一些PRRSV-1和类欧洲毒株只能使用肺泡巨噬细胞进行分离。
Since cytopathic effects, which occur in 1-4 days, are not always clear, virus isolation usually needs to be confirmed by RT-PCR, IPMA or IFA (maximum sensitivity at 7 days). Virus titration can be done using serial dilutions of sample. 由于在1-4天内发生的细胞病变效应并不总是清楚的,病毒分离通常还需要通过RT-PCR、IPMA或IFA(7天时最为敏感)来确认。而病毒滴定可以使用连续稀释的样品的方法进行测定。

(未完待续)
版权归原作所有,向作者致敬,如有侵权,请联系删除。


{{item.content}}